IWMS (integrated workplace management system) software provides a central platform for managing and coordinating various workplace functions, such as facilities management, real estate management, asset management, and space management.
What is an Integrated Workplace Management System (IWMS)?
An IWMS is a unified software solution that integrates multiple facility and real estate management functions into a single, centralized platform. Unlike traditional facility management tools that operate in silos, modern workplace management tools like IWMS, provide end-to-end visibility and control over all aspects of workplace operations, from space planning and asset tracking to maintenance scheduling and energy management.
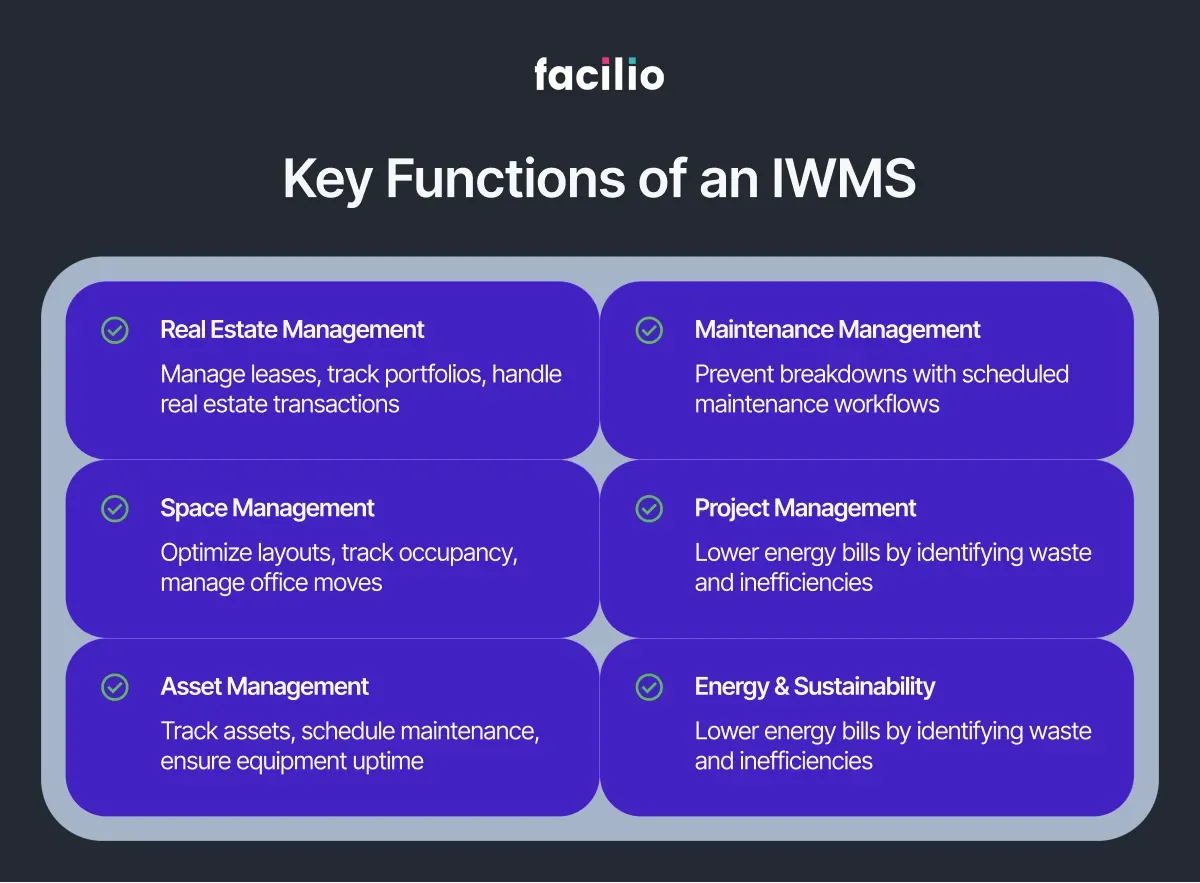
Core Components of IWMS:
- Real Estate Management: Portfolio optimization, lease administration, and strategic planning
- Space Management: Utilization analytics, desk booking, and flexible workspace configuration
- Maintenance Management: Predictive maintenance, work order automation, and asset lifecycle tracking
- Asset Management: Equipment tracking, procurement, and performance monitoring
- Sustainability Management: Energy monitoring, ESG reporting, and environmental compliance
- Employee Experience Management: Mobile access, service requests, and workplace analytics
A brief history of IWMS software
IWMS software has a relatively long history, with the first systems dating back to the 1980s.
The concept emerged as a way to provide a central platform for managing and coordinating various workplace functions.
Today, IWMS software is widely used by various organizations, including businesses, government agencies, educational institutions, healthcare organizations, and nonprofit organizations.
Key Features and Capabilities of Modern IWMS

1. AI-Powered Space Optimization
Advanced IWMS platforms leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze space utilization patterns, predict future needs, and automatically optimize workspace layouts. These systems can increase space efficiency by up to 40% through data-driven insights and recommendations.
2. Real-Time Asset and Maintenance Management
Modern IWMS solutions integrate IoT sensors and predictive analytics to monitor asset health continuously, schedule preventive maintenance automatically, and reduce facility maintenance costs by up to 14%. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected breakdowns and extends asset lifecycles.
3. Cloud-Based Deployment and Scalability
Cloud deployment is advancing at a 17.40% CAGR due to subscription pricing models, rapid implementation capabilities, and scalability advantages. Cloud-based IWMS platforms enable organizations to manage multiple locations from a centralized dashboard while supporting remote and hybrid work arrangements.
4. Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence
Contemporary IWMS platforms provide comprehensive analytics capabilities, including:
- Real-time occupancy tracking and utilization heatmaps
- Predictive modeling for space and resource planning
- Cost analysis and budget optimization tools
- Performance benchmarking against industry standards
- Custom reporting and dashboard creation
5. Mobile-First Employee Experience
Modern IWMS solutions prioritize mobile accessibility, enabling employees to:
- Book desks, meeting rooms, and parking spaces
- Submit maintenance requests and service tickets
- Navigate buildings using indoor mapping and wayfinding
- Access building information and amenities
- Receive real-time notifications and updates
6. ESG and Sustainability Management
IWMS platforms automatically aggregate energy, water, and emissions data, generate audit-ready reports, and surface efficiency projects that lower costs and carbon footprints. This capability is crucial for organizations pursuing net-zero targets and ESG compliance requirements.
How has COVID-19 influenced the way IWMS solutions are used?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the way that organizations use IWMS software. Many organizations have had to adapt their use of IWMS software to meet the challenges posed by the pandemic, including:
- Remote work: The shift to remote work has led many organizations to use IWMS software to manage and optimize the use of virtual workspace and resources, such as virtual meeting rooms and hybrid work tools.
- Return-to-work planning: As organizations begin to plan for the return to work, they are using IWMS software to manage and coordinate the process, including tasks such as scheduling and resource management, move management and space planning, and asset tracking and inventory management.
- Social distancing and safety measures: Organizations are using IWMS software to manage and implement social distancing and safety measures, such as reducing the number of people in a space at any one time and tracking the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Cleaning and sanitization: Organizations are using IWMS software to schedule and track cleaning and sanitization tasks and monitor and report on the use of cleaning and sanitization products.
How different industries use IWMS software
Various organizations in different industries use IWMS software. Some examples of industries that use IWMS software include:
- Private businesses: Many businesses, including large multinational corporations (MNCs) and smaller companies, use IWMS software to manage and optimize the use of their physical workspace and resources. It is useful for organizations with multiple locations or a large, complex physical workspace.
- Government agencies: Government agencies at the local, state, and federal level use IWMS software to manage and optimize the use of their facilities and resources. This includes tasks such as scheduling and resource management, real estate and lease management, and maintenance and repair management.
- Educational institutions: IWMS software is commonly used by schools, colleges, and universities to manage and optimize the use of their physical workspace and resources. This involves scheduling and resource management, move management and space planning, asset tracking, and inventory management.
- Healthcare organizations: Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare organizations use IWMS software to manage and optimize the use of their facilities and resources. This includes tasks such as scheduling and resource management, real estate and lease management, and maintenance and repair management.
- Nonprofit organizations: Nonprofit organizations, such as charities and advocacy groups, use IWMS software to manage and optimize the use of their physical workspace and resources. These are tasks such as scheduling and resource management, move management and space planning, asset tracking, and inventory management.
Implementing IWMS software

Here are some steps to follow when implementing IWMS software in an organization:
- Identify your needs and goals: Before implementing IWMS software, it is important to identify your organization's specific needs and goals. This will help you to determine which features and capabilities are most important and will inform your decision about which IWMS software to use.
- Research and compare options: There are many different IWMS software options available, so it is important to research and compare different options to find the one that best meets your organization's needs and goals. Consider factors such as cost, features, scalability, and customer support when making your decision.
- Plan your implementation: Once you have selected an IWMS software, you will need to plan your implementation. This will involve determining how you will roll out the software, who will be responsible for implementing and managing it, and how you will train users on the new system.
- Set up and configure the IWMS software: Next, you will need to set up and configure the IWMS software. This will involve installing the software, setting up user accounts, and configuring the system to meet your organization's specific needs and requirements.
- Test and train users: Before going live with the IWMS software, it is important to test the system and train users on how to use it. This will help to ensure that the system is functioning properly and that users are familiar with its capabilities and how to use it effectively.
- Go live with the IWMS software: Once you have tested the system and trained users, you are ready to go live with the IWMS software. This will involve transitioning from your current system to the new IWMS software and involves data migration and other tasks.
- Monitor and maintain the IWMS software: After implementing the IWMS software, it is important to monitor and maintain the system to ensure that it is functioning properly and meeting your organization's needs. This involves periodic software updates, user training, and other tasks.
Benefits of IWMS software

There are several benefits to using IWMS software in an organization, including:
- Improved utilization of physical workspace and resources: Organizations can better utilize their physical workspace and resources, such as conference rooms, desks, and equipment. By providing scheduling and resource management tools, IWMS software helps reduce the number of unused or underutilized resources and improve the efficiency of their workspace.
- Reduced costs: For example, by using IWMS software to schedule and manage conference rooms and other resources, organizations can reduce the number of unused or underutilized resources, resulting in cost savings.
- Increased productivity: Organizations can increase productivity by providing scheduling and resource management tools and tracking and managing work orders and contracts. By optimizing the use of physical workspace and resources, companies can reduce the time and effort required to complete tasks, leading to increased productivity.
- Better decision-making: You get access to data analysis and reporting tools, which helps organizations make better-informed decisions about their physical workspace and resources. This helps identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement and make more informed decisions about their workspace and resources.
- Improved communication and collaboration: IWMS software helps organizations improve communication and collaboration by providing a central platform for scheduling and resource management and tools for tracking and managing work orders and contracts. By improving communication and collaboration, organizations can reduce the risk of errors and delays and improve the efficiency of their operations.
Overall, IWMS software provides organizations with a wide range of benefits by helping them better manage and optimize their physical workspace and resources.
CAFM vs. IWMS software
CAFM (Computer-Aided Facility Management) and IWMS (Integrated Workplace Management System) are both types of software that are used to manage and optimize the use of physical workspace and resources in an organization. However, there are some key differences between the two:
- Scope: IWMS software typically provides a more comprehensive range of tools and features for managing and optimizing the use of physical workspace and resources. It typically includes real estate and lease management tools, space planning, asset tracking, energy, and environmental monitoring, and facilities management. CAFM software, is more related to facility management software, such as maintenance and repair management and does not include all of the features found in IWMS software.
- Integration: IWMS software is designed to provide a single, integrated platform for managing and coordinating various workplace functions. It is typically designed to provide a seamless flow of data and information between different modules, such as space and resource scheduling, real estate management, and asset tracking. CAFM software, on the other hand, is more focused on specific facilities management tasks and does not provide the same level of integration with other workplace management functions.
- Customization: IWMS software is typically more flexible and customizable than CAFM software. It is designed to be able to handle a wide range of different workplace management scenarios and requirements and can be customized to meet the specific needs of different organizations. CAFM software, on the other hand, is more limited in terms of customization options.
Want to learn more about the best IWMS solution for your business? Get in touch, today!












