Mastering CARB Refrigerant Regulations: Essential Guide for Facility Managers
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) lays down stringent regulations to govern the use, emissions, and management of refrigerants.
Like most refrigerant regulations, CARB is also designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect air quality, and promote sustainable practices within industries that utilize refrigerants.
If you are a facilities or operations manager of a property in California where refrigerants are frequently used, understanding and complying with these requirements is mandatory.

CARB refrigerant requirements 101
First, let’s understand what CARB is and what its role is in environmental regulations.
There are three primary objectives that the board addresses:
- Implement regulations to control air pollutants
- Conduct research on air pollution control efforts in California
- Provide guidance to businesses in the state that use air pollutants like refrigerants
Incidentally, the management of refrigerants, the use of which might release potent greenhouse gasses, is one of the key focus areas for CARB.
CARB provides specific guidelines for the use of refrigerants, their emissions, and reporting and documentation. Here is an overview
Specific regulations for types of refrigerants used
CARB regulates the use of high-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, encouraging the transition to low-GWP alternatives. Additionally, the body is also extending incentives in support of low-GWP alternatives.
Thresholds and limits on refrigerant emissions
CARB implements and enforces the California’s cap-and-trade program, which has emission reduction targets as follows:
- 40% below 1990 levels by 2030
- 80% below 1990 levels by 2050
Phasedown schedule: CARB established a phasedown schedule for the use of high-GWP refrigerants in the early 2000s and has been promoting the adoption of low-GWP alternatives.
As per the schedule, businesses were required to register and report to the board before 2016. Since the registration deadlines closed in 2016, it is now mandatory for all facilities using refrigerants to report and register with CARB immediately.
Reporting and documentation requirements for compliance
The following reporting requirements revolve around record-keeping, certification, training of personnel, and annual reporting.
- Record-keeping: Detailed records of all refrigerant purchases, their usage, and scheduled and reactive leak inspections/repairs/replacements must be maintained.
- Certification and training: All personnel handling refrigerants must be certified and trained according to CARB standards.
- Annual reporting: Facilities must submit annual reports detailing the above to CARB on an annual basis.
CARB regulations and the resulting challenges for property operations
Undoubtedly, being compliant with these regulations is an additional responsibility that demands time and resources. Facility and operations managers who are already pressed for both will find this challenging.
Facility managers face several challenges in adhering to CARB refrigerant regulations:
- Complex reporting requirements: For a veteran as well as a rookie facility manager, the reporting requirements of CARB can be overwhelming, especially if the business has a chain of several facilities spread across multiple locations and geographies.
- Transition to low-GWP refrigerants: Replacing the current inventory of high-GWP with low-GWP alternatives can be costly and logistically challenging.
- Leak detection and repair: Conducting scheduled leak inspections and repairs across single or multiple properties requires significant investment in technology and personnel training.
- Training and certification: Recruiting certified staff will prove to be challenging. Training existing staff and helping them become certified is also time-consuming and expensive.
However, facility managers can take comfort in the fact that adhering to these regulations does accrue certain benefits.
Case study: How Tuten Labs Leverages Facilio to Digitize & Automate O&M across 10,000 Large Format Retail Stores
Tuten Labs is a Georgia-based technology leader helping retail stores reduce energy consumption and deliver a consistent in-store experience for end customers.
Tuen Labs lacked a centralized remote monitoring system which led to several challenges like:
- Alarm fatigue and slow response times
- Time-consuming manual alarm reconciliation
- Manual and error-prone work order process
Facilio's Solution - Unified Monitoring + Maintenance & Streamlined Operations
Partnering with Facilio enabled Tuten labs to solve their challenges while improving operational efficiency. Here is how Facilio helped:
- Energy management: Enhanced energy management contributes to overall reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with CARB's requirements.
- Proactive monitoring: 24/7 predictive monitoring and fault detection help in early identification and repair of refrigerant leaks, ensuring compliance with CARB’s stringent leak detection and repair standards.
- Scalable compliance reporting: Facilio, with its automated report generation allows Tuten to prepare reports easily that comply with CARB and several other regulations in the US.

Compliance strategies for enterprise portfolio managers
Complying with CARB or any environmental regulation requires having a comprehensive strategy. It mandates the bringing together of people, technology, and processes.
Strategies will vary from business to business depending on their refrigerant usage and complexity of operations. The generic strategy given below suits most businesses and can act as a starting point for your compliance strategy.
1. Regular audits and refrigerant management plans
Conducting regular audits and managing refrigerants is the first crucial step in strategy formulation. You can approach this in three steps:
Step 1: Conduct an initial audit
An initial audit should be conducted to gain an understanding of the current refrigerant usage, equipment inventory, and compliance status. The audit should aim to identify areas with the highest refrigerant emissions or where frequent leaks are reported. This would also be an ideal juncture to decide on the methods of leak detection and set a baseline for future refrigerant usage and emissions.
Step 2: Create a refrigerant management plan
As the next step, define SMART goals for reducing refrigerant emissions and leaks. This should be supported by a leak detection and repair (LDAR) program that will assign responsibilities to personnel and also set the schedule for inspections and preventive maintenance.
Step 3: Perform regular audits
While the initial audit gives an overview of the state of affairs, regular audits (monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually) help in the early detection of issues and ongoing compliance. The audit findings will also help calibrate the current refrigerant management plan and ensure it complies with evolving CARB regulations.
2. Technology and tools for monitoring and managing refrigerant use
Given the volume and variety of refrigerants used, it is important to invest in technology and tools to monitor and manage its usage. Also, it is necessary to invest in connected refrigeration systems that can consolidate data in one place and give a bird’s eye view of compliance for the business as a whole.
These tools should help with three major activities:
II. Day-to-day monitoring
For day-to-day monitoring of refrigerant systems and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, internet of things (IoT) devices are the ideal option. These small sensors have long battery life and can be attached to surfaces to monitor refrigerant levels, detect leaks, and assess system performance effectively.
III. Automated reporting and compliance
All the data from IoT sensors and cloud platforms should be consolidated in one location for easy access and analysis. There are refrigerant compliance and leak detection software, such as Facilio, that can automate the generation and submission of required CARB compliance reports.
III. Data analytics and visualization
The same tools can help in regularly reviewing data to identify trends, inefficiencies, or areas for improvement. They can be used to implement data-driven changes to improve refrigerant management practices and reduce emissions.
3. Stakeholder management and engagement
CARB requirements mandate technicians to be certified and to follow specific procedures while repairing or replacing refrigerant equipment.
Technical education and work experience prepares them for the task to a certain extent. However, continuous learning and training is necessary to keep them sharp and updated with the latest statutory requirements.
Also, there is the organizational need to instill a sense of stakeholder responsibility where each personnel thinks, acts, and works in a way that is efficient, productive and compliant.
This calls for extensive training and also provides the necessary tools for maintenance teams.
This can be accomplished in the following ways:
Step 1: Develop a training program
- Assess the current knowledge and skills of maintenance teams related to refrigerant management and CARB regulations. Conduct an inventory check for gaps in certification, expiry, or renewals of existing maintenance teams.
- Develop comprehensive training materials, including manuals, online courses, and hands-on workshops to upskill the team.
Step 2: Conduct training sessions on CARB
Give a walkthrough of CARB and its requirements to the stakeholders. Highlight why compliance is important, the downside of non-compliance, like fines and penalties and its role in upholding sustainability.
Additionally, the maintenance teams and related stakeholders must also be made aware of how to use modern software to have portfolio-wise visibility as well as granular level visibility of tasks like work orders to keep operations running smoothly.
Step 3: Foster a Culture of Compliance
Instill a culture of safety and compliance amidst maintenance teams. This requires setting the tone from leadership and emphasizing on the need for lowering energy consumption, improving sustainability, and reducing operational costs.
Role of AI/IoT in streamlining refrigerant compliance
Artificial intelligence (AI) and IoT have replaced traditional methods of managing refrigerant compliance. They provide advanced tools for real-time monitoring, data analysis,and optimized refrigerant use, all the while ensuring that facilities remain compliant with regulatory requirements like CARB.
Further, they also automate compliance tracking and reporting, thus saving facility managers effort and time.

Benefits of integrating AI into property operations for compliance and efficiency
Property operations require specific recurring activities to work with clockwork precision. Scheduled maintenance, work order creation, and compliance report generation are some common use cases.
When these operations are run manually, they are prone to several downsides. To begin with, the manual process is slow and time-consuming. Also, human intervention leads to inconsistencies, errors, and often non-compliance as well.
Leveraging IoT in property management can provide several benefits:
1. Real-time monitoring and data collection
IoT sensors provide continuous monitoring of refrigerant levels, system performance, and environmental conditions without requiring technicians to manually visit the equipment location and make readings.
AI algorithms can analyze the log data in real time and also generate immediate alerts in case of leaks, system malfunctions, or compliance breaches. This enables swift corrective actions for high-priority tasks while routine checks are considered for resolution at a later time.
2. Predictive maintenance instead of reactive maintenance
IoT facilitates optimizing maintenance based account actual equipment performance instead of scheduled maintenance. While scheduled maintenance has its own advantages, predictive maintenance would be a better approach to fixed intervals which may not be necessary or sometimes too late to detect issues and fix them.
Refrigerant leaks, if left unchecked over a period of time, can accumulate hefty costs, both in terms of repairs and fines for non-compliances.

3. Prioritized alarm management
IoT sensors broadcast a steady stream of alarms for even the slightest anomaly, which in turn can overwhelm technicians and facility managers. However, only a minority of these notifications would be priority notifications requiring immediate intervention.
IoT-based remote monitoring systems can be paired with historical data of equipment and highlight only those notifications that are of high-priority. This prioritized alarm management makes operations easier and smoother for facility managers.
4. Data-driven equipment management
CARB and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) at large recommends repairing or replacing equipment if their leak rates exceed threshold. IoT sensors provide real-time data which can be further analyzed to derive trends in refrigerant consumption, leak rates, and repairs. This facilitates data-driven decision-making for equipment management.
5. Environmental and financial benefits
Last, but not the least, all the above-mentioned benefits ultimately lead to operational efficiency and cost savings. The cost of reduced energy consumption, fewer repairs, and lower regulatory penalties when calculated on an annual basis cannot be ignored.
How Facilio can help you with CARB compliance
Facilio leverages AI and IoT technologies to provide a comprehensive solution for managing refrigerant compliance. It takes the form of a connected refrigeration solution that can detect leaks, ensure reporting compliance, and optimize refrigeration management across multiple sites.
With Facilio you can consolidate all refrigeration operations under one system and eliminate dependencies on disparate systems that create data silos.
Its key features include:
1. Centralized refrigerant management
Facilio’s unified dashboard offers a centralized dashboard that provides a real-time view of refrigerant levels, usage, and emissions across all facilities.
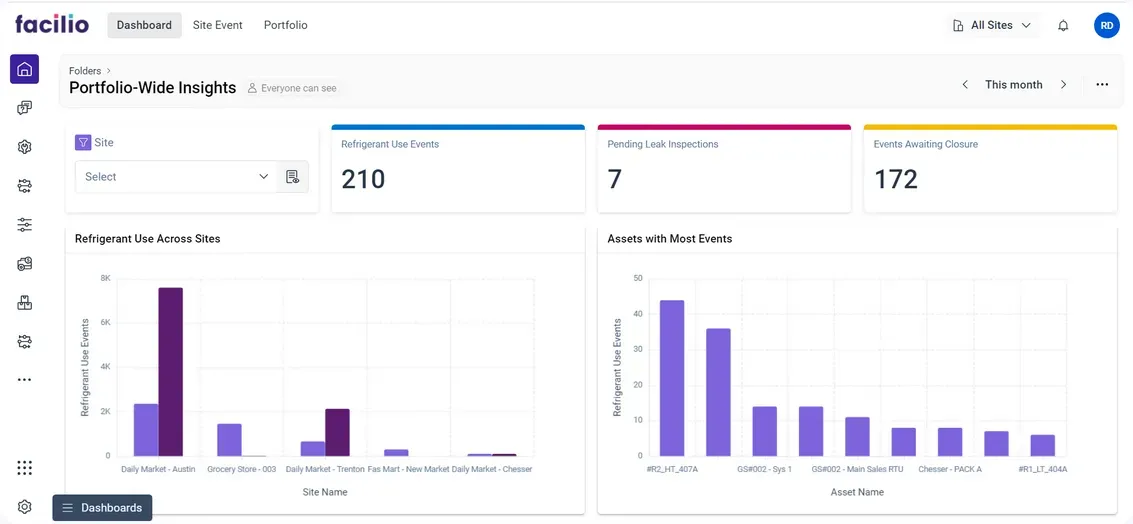
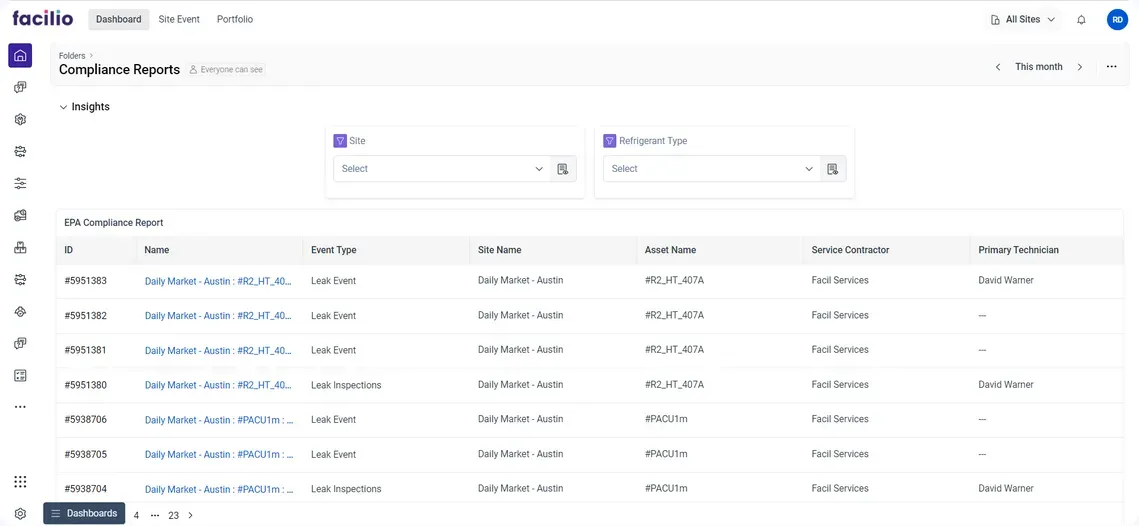
2. Automated compliance reporting
Facilio automates the creation and submission of compliance reports including CARB, ensuring they meet all legal requirements and timely submission. Further, the platform also maintains accurate and detailed records of all necessary transactions, like leak repairs, equipment replacements, personnel training and certification, etc.
3. Predictive analytics and maintenance
Facilio’s AI algorithms analyze historical and real-time data to predict potential leaks and system failures, allowing for proactive maintenance. It also integrates data from IoT sensors, building management systems, and manual entries, ensuring all information is accessible in one place.
4. Leak detection and alerting
Facilio’s IoT-enabled sensors detect refrigerant leaks in real time and trigger alerts to facility managers for emergency actions. You can also keep track of equipment health and view leak repairs completed across all locations in one place.
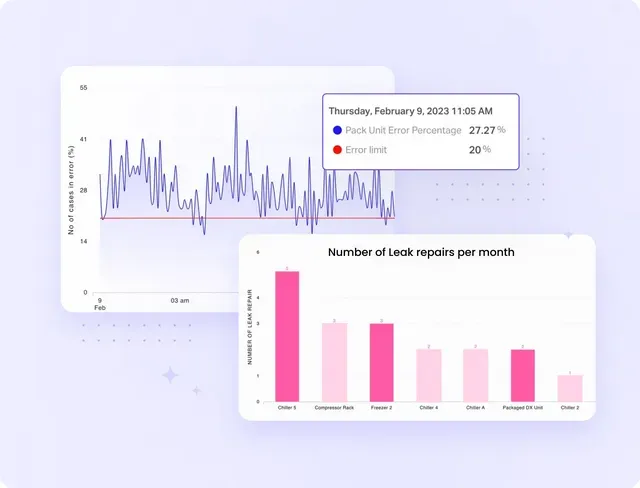
5. Sustainability and efficiency improvements
By ensuring compliance and optimizing refrigerant management, Facilio helps facilities reduce their environmental footprint. The streamlined processes also contribute to improved operational efficiency, leading to cost savings.
CARB: Future trends, their impact, and how to prepare
CARB regulations were introduced in 1967. It has been amended several times to stay abreast with times and also to ensure stricter adherence. There are also several trends in the horizon that can potentially change how organizations currently use and manage their refrigerants and electrical equipment.
Lower GWP limits are being introduced
Lowering allowable GWP thresholds for refrigerants is a high priority for the EPA and CARB.
Impact:
Organizations will have to phase out high-GWP refrigerants and transition to low-GWP alternatives that are environment-friendly. This might require system updates, retro fitting, or in some cases even replacements.
Source: Frequent Questions on the Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons | US EPA
How to prepare:
Develop a systematic plan to upgrade, repair, or replace non-compliant equipment or refrigerants that could be non-compliant with GWP thresholds.
Increased reporting and audits
Compared to EPA, CARB has stringent and complex reporting requirements which are revised from time to time. Facility managers will have to keep a close watch on changing regulations and reporting requirements.
Impact:
Monitoring and reporting capabilities will have to be upgraded requiring new investments in cloud-based software that will auto-generate compliance reports.
How to prepare:
Use cloud-based automated systems to track all regulatory compliances across all locations remotely. Digitize all manual record-keeping activities to avoid non-compliance and erroneous reporting.
Tougher standards for leak detection and repair standards
EPA recommends best practices for leak detection and repairs. These standards, akin to reporting requirements, are revised periodically to keep leak rate calculations consistent. As these standards get tougher, organizations will have to revise their leak rate calculations and choice of methods as well.
Impact:
Robust leak detection and repair programs will have to be implemented, which could incur higher capital outlay for new equipment and training.
How to prepare:
Create awareness amidst technical personnel through continuous training. Develop an organization-wide system of leak calculations, reporting, and compliance.
In a nutshell: CARB and refrigerant compliance
CARB regulations were introduced to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and establish best practices to mitigate air pollution threats.
Its compliance ensures that facilities contribute positively to environmental protection, while avoiding regulatory penalties. In the bigger scheme of things, it also makes the organization support sustainability goals while improving their operational efficiency.
Facilio’s AI-driven platform offers a centralized solution for tracking, reporting, and reducing refrigerant emissions. It leverages IoT sensors and cloud technology for real-time monitoring and reporting of data. AI algorithms aid in real-time data analysis and automation, empowering facility managers to optimize their operations while ensuring regulatory compliance.
More from Facilio















