Visual inspection has been a reliable way for maintenance teams to spot cracks, corrosion, leaks, and early-stage failures for years. As facilities become more complex, advanced visual inspection - powered by digital checklists, high-resolution imaging, and AI-assisted detection - helps improve accuracy, standardize inspections, and reduce the risk of missed issues.
So what does modern visual inspection look like in maintenance, and how does it strengthen reliability across facilities?
This blog outlines what visual inspection looks like in maintenance today - the types and steps involved, the challenges teams face, and how digital tools and CMMS platforms make inspections more accurate and reliable.
What is visual inspection?
Visual inspection is a form of non-destructive testing (NDT) used in many industries to check the quality and integrity of products, components, and systems. In facilities management, it plays a crucial role by helping teams spot early signs of defects - such as cracks, corrosion, or leaks, through simple visual checks before they escalate into costly repairs or downtime.
Traditionally, it’s about directly observing an object or process to spot defects or anything that doesn’t meet the required standards. Today, visual inspection has evolved so much incorporating tools like artificial intelligence (AI) and remote imaging to improve both accuracy and efficiency.
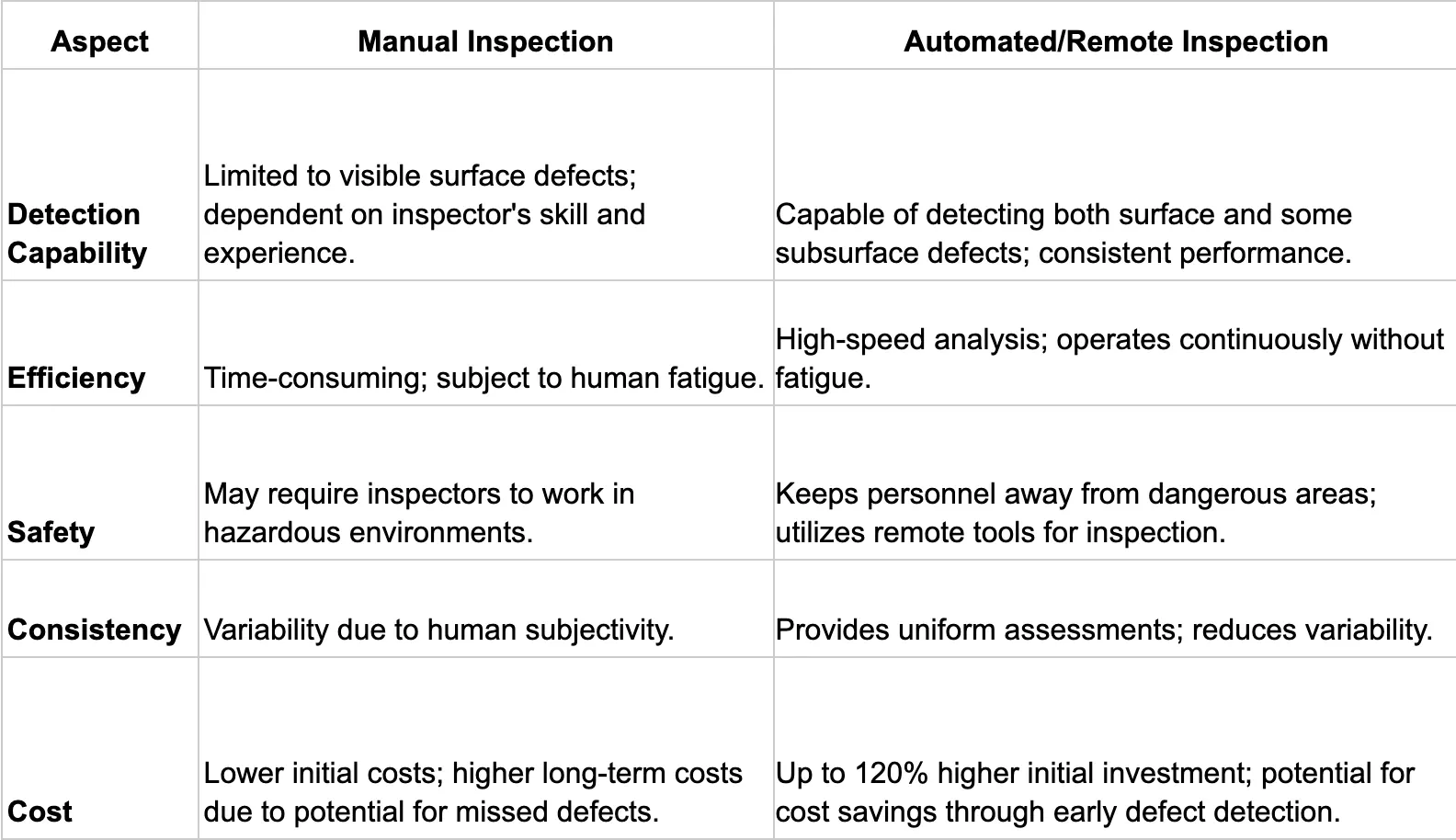
Types of visual inspection - Traditional vs automated/remote visual inspection
Visual inspection today falls into two main types: traditional manual inspection and modern digital or remote visual inspection. Manual checks rely on the human eye, while digital tools-like AI, high-resolution imaging, drones, and robotic cameras-make inspections more accurate and safer.
Why is visual inspection so important?
Visual inspection is crucial for maintaining product and system quality, safety, and efficiency. In maintenance inspection workflows, these visual checks act as the first line of defence against equipment wear, leaks, or early-stage failures. By consistently identifying defects and inconsistencies, it forms the foundation of quality control and maintenance.
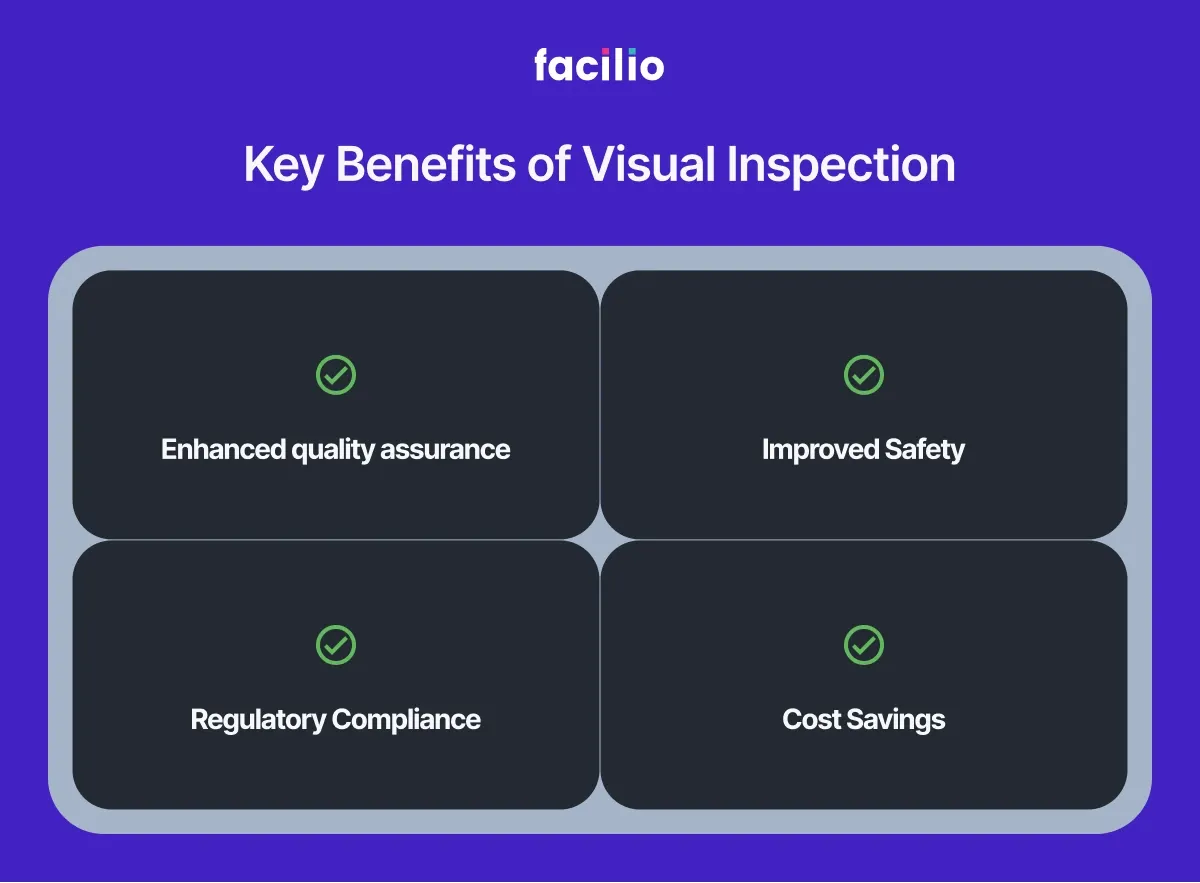
Key benefits of visual inspection
- Enhanced quality assurance: Detecting defects early in the production process helps maintain high-quality standards and prevents defective products from reaching the market.
- Improved safety: Regular inspections uncover potential hazards, enabling quick action to prevent accidents and promote a safer workplace.
- Regulatory compliance: Ongoing visual inspections ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, reducing the risk of costly penalties.
- Cost savings: Identifying defects early on minimizes the need for expensive repairs and cuts down on waste, leading to significant savings.
A connected maintenance platform helps teams:
1. Use standardised digital checklists so every inspection follows the same steps.
2. Capture photos, notes, and readings on mobile during walk-throughs and store them in one place.
3. Convert inspection findings into work orders instantly, avoiding scattered spreadsheets or emails.
4. Track recurring defects and prioritise maintenance based on real inspection data.
This transforms visual inspections from isolated tasks into a consistent, repeatable, and traceable process across sites.
Key techniques in visual inspection
Visual inspection is critical for quality control, ensuring that products and systems meet set standards. Over the years, new techniques have improved the accuracy and efficiency of visual inspections, including:
- Surface Inspection - It focuses on identifying visible defects like scratches, dents, cracks, or discoloration. Traditionally done manually, it has now been enhanced by automated systems using high-resolution cameras and image-processing algorithms to spot even the smallest imperfections.
Example: In the automotive industry, surface inspection systems detect paint defects to ensure vehicles meet both aesthetic and quality standards. - Dimension Inspection - This involves checking the size, shape, and alignment of products to ensure they meet design specifications. Automated systems using laser scanners and optical tools improve accuracy, reducing human error and boosting production speed.
Example: In semiconductor manufacturing, dimension inspection ensures microchips fit perfectly into electronic devices. - Statistical Process Control (SPC) SPC uses statistical methods to monitor and control processes, helping manufacturers detect variations and make adjustments to maintain product quality. Integrating SPC with visual inspection provides real-time monitoring and the ability to act quickly. Example: In textile manufacturing, SPC monitors fabric quality to ensure consistency in texture and color across production runs.
- Computer Vision Computer vision leverages AI to analyze visual data, allowing machines to detect patterns and anomalies that may be difficult for human inspectors to spot.
Example: In the food industry, computer vision systems are used to check the ripeness and quality of fruits and vegetables, automating the inspection process. - Predictive Analytics Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning to forecast potential defects or failures, enabling proactive maintenance and quality checks.
Example: In aerospace manufacturing, predictive analytics helps anticipate wear and tear on components, allowing for timely maintenance before issues arise.
What are the common challenges in visual inspection?
Visual inspection is a key part of quality assurance across industries, but it’s not without its challenges:
- Human error: Manual inspections can suffer from inconsistencies caused by fatigue, subjective judgment, and simple oversight.
- Limited to surface-level issues: Traditional methods often miss internal or subsurface defects, focusing only on visible problems.
- High costs of automation: For small and medium businesses, upgrading to automated systems can feel like a financial stretch.
Understanding these issues and addressing them with smart solutions can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency. (Source: U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information)
Solutions to overcome challenges in visual inspection
- Better training programs:
- Offer detailed training to sharpen inspectors’ skills and minimize mistakes.
- Keep training materials fresh by including the latest techniques and standards.
- Advanced tools:
- Use tools like drones and borescopes to reach tricky areas and catch hidden defects.
- Leverage AI and machine learning to spot issues that might escape human eyes.
- Affordable automation:
- Opt for scalable, budget-friendly automation tailored for smaller businesses.
- Roll out automation in phases to spread out costs and give teams time to adapt.
- Integrate with a Connected CMMS software:
- Implement CMMS to standardize processes and make documentation a breeze.
What are the steps involved in Visual Inspection?
Implementing a structured visual inspection process is essential for maintaining quality and safety standards across various industries. Below is a step-by-step guide to conducting effective visual inspections:
1. Preparation
- Define inspection criteria: Clearly outline what constitutes a defect or non-compliance.
- Gather necessary tools: Ensure all required inspection tools and personal protective equipment (PPE) are available and in good condition.
- Review documentation: Familiarize yourself with relevant manuals, standards, and previous inspection reports.
2. Inspection
- Initial observation: Conduct a general overview to identify any obvious issues.
- Detailed examination: Inspect specific components or areas systematically, following a predetermined sequence.
- Use of aids: Employ magnifying glasses, mirrors, or other tools to enhance visibility in hard-to-reach areas.
3. Documentation
- Record findings: Note all observations, both compliant and non-compliant, with detailed descriptions.
- Capture visual evidence: Take photographs or videos of identified issues for reference.
- Utilize checklists: Use standardized checklists to ensure consistency and completeness.
4. Reporting
- Compile report: Summarize findings in a clear and concise report, highlighting critical issues.
A strong visual inspection summary usually covers:
Context: Asset name/ID, location, date, inspector, and why the inspection was done.
Overall condition: One–two lines stating whether the asset is acceptable, needs monitoring, or requires repair.
Key findings by severity: Start with critical issues, then minor defects, using short, clear statements.
Evidence: Refer to supporting photos or attachments (for example, “See Photo 3- corrosion on pipe joint”).
Recommended actions and timelines: What needs to be done, by whom, and by when.
- Recommend actions: Suggest corrective measures for identified problems.
- Distribute to stakeholders: Share the report with relevant personnel for review and action.

How does Facilio’s Connected CMMS standardize visual inspections?
Integrating a Connected Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) like Facilio’s into your visual inspection process takes efficiency and accuracy to the next level.
During preparation, Facilio’s CMMS lets you create and store detailed checklists and flowcharts, so inspectors have everything they need right at their fingertips.
When it comes to inspections, the mobile-friendly CMMS platform (with offline access support) allows real-time data entry even in low-network areas making it easy to document findings on the go.
It centralizes all inspection data-from photos to notes-into an accessible digital record, and when it’s time to report, it automates analytics to spot recurring issues and shape smarter maintenance strategies. With Facilio’s Connected CMMS, you can streamline inspections, cut down errors, and ensure top-notch quality every time.
Book a 1:1 demo of Facilio to see how a Connected CMMS can simplify and standardize your visual inspection process.
Get started now!
Ready to explore how visual inspection can be standardized and streamlined with a Connected CMMS?
Frequently Asked Questions
Visual inspection is a technique for detecting defects by using the naked eye to check whether equipment is working properly and whether manufactured products meet their specifications. It can be carried out in person or remotely by reviewing photos or other digital images.
The basic steps are: prepare by defining criteria and reviewing documentation; inspect the asset in a structured sequence; document all findings with notes and photos; and report results so corrective actions or work orders can be created.
The commonly used fields include manufacturing, construction, building maintenance, electrical systems, oil and gas, and aerospace where early detection of visible defects is critical.











