
Accurate EPA Refrigerant Leak Detection, Calculation & Leakage Cost in 2025
Refrigerant leaks aren’t just a minor hiccup—they drive up costs, hurt the environment, and can lead to hefty fines.
The EPA estimates that if all food retailers kept leaks at GreenChill standards, the industry could save $96M a year on refrigerant alone.
A Star Refrigeration study found that some systems lose 20% of their charge annually due to poor design and maintenance, leading to wasted energy and higher carbon emissions.
So, quite evidently, tracking and managing leak rates isn’t optional—it’s the key to cutting costs and keeping your system efficient.
This guide breaks down how to calculate refrigerant leak rates, when and why to track them, and best practices for maintenance and record-keeping. We’ll also cover key regulations to help you stay compliant and keep your HVAC systems running at peak efficiency.
But before proceeding, let’s understand why accurate refrigeration leak rates matter.
Refrigerant leakage: Why is accurate calculation so crucial
Calculating and monitoring refrigerant leak rate is imperative and non-negotiable for several reasons, like
a) Higher Energy Costs: Unchecked refrigerant leaks lead to increased energy consumption, driving up energy bills.
b) Preventing Major System Damage: Addressing leaks early helps avoid severe damage to your AC system, extending its lifespan.
c) Environmental Impact: Refrigerants can harm the ozone layer and contribute to global warming, making leak prevention crucial for the environment.
d) Health Risks: Certain refrigerants can be harmful to human health, especially if there is exposure to leaks.
e) Regulatory Compliance: Many regions enforce strict regulations on refrigerant leak levels, requiring accurate calculations and proper documentation.
Every retail store manager or multi-site facility manager has to deal with the menace of refrigerant leaks. Leak rates need to be calculated and measured primarily to be in compliance with EPA regulations relating to refrigerant compliance.

There are specific sections, like Section 608, that lay down compliance requirements, and also records of leak rate calculations are to be maintained.
From an operational perspective, the damage that these leaks create is twofold:
- They compromise the efficiency of the overall HVAC system.
- They could incur hefty fines up to $37,500 per day for any violation of these regulations.
This necessitates understanding and learning how to manage refrigerant leaks. This is where a HVAC refrigerant leak rate calculation comes into play.

Getting started with calculating refrigerant leak rates
The first step in calculating the leak rate is to record the refrigerant charge accurately. This is often referred to as the “baseline measurement” and determines whether your leak rate is under control or exceeds approved limits.
Once this is done, follow the steps below to accurately calculate your refrigerant leak rate.
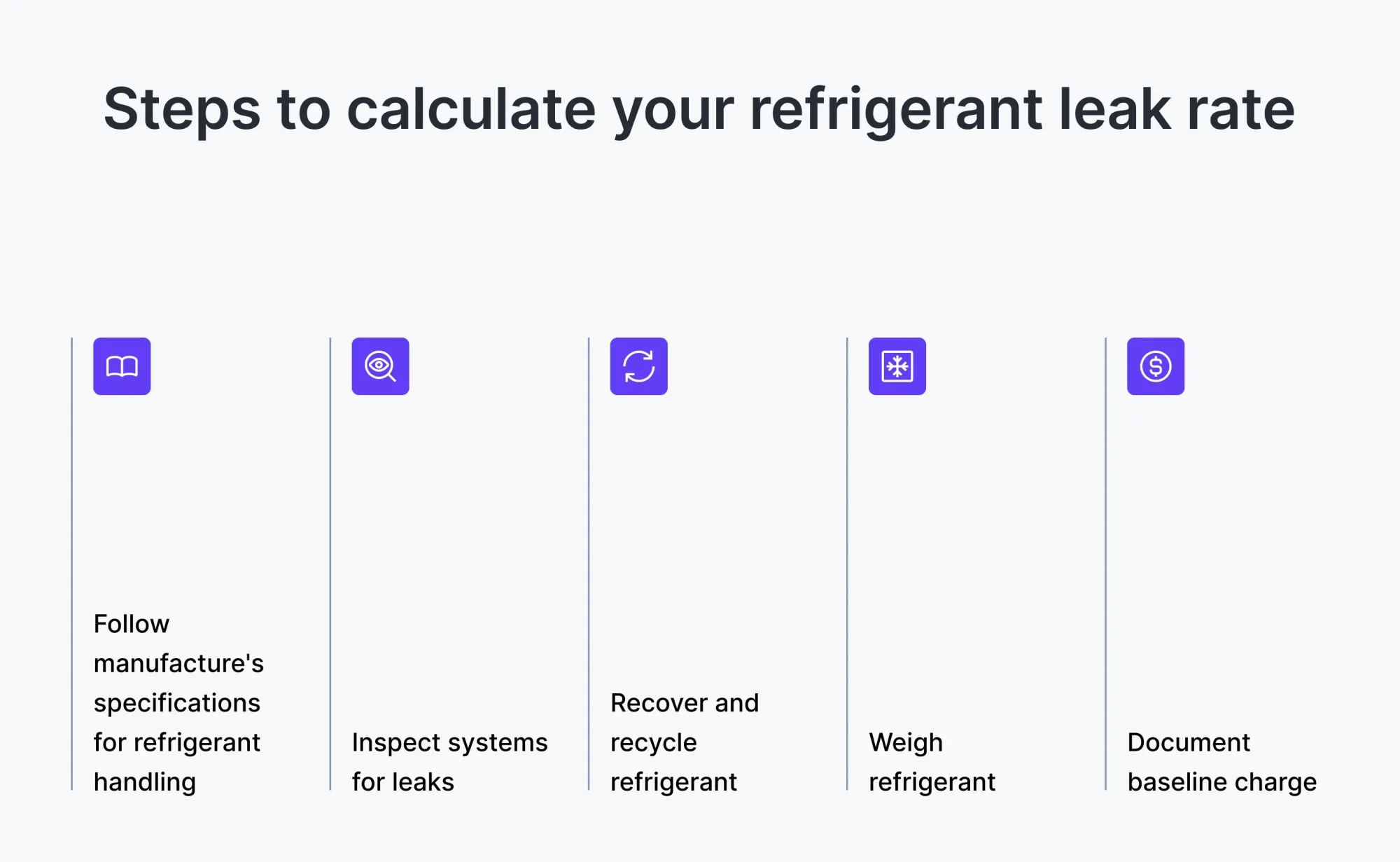
a) Follow the manufacturer’s specifications
Most HVAC manufacturer manuals come with recommended refrigerant charge levels and specific procedures for charging. Make a note of the recommended charge level from the same to compare it with the current charge.
b) Inspect the system for existing leaks
Before adding or adjusting the refrigerant, inspect and ensure that the system doesn’t show any signs of leaks. Even a new AC unit could have leaks if it had factory defects that were not detected and fixed.
c) Recover and recycle existing refrigerant
If the current refrigerant charge level is in excess of the recommended level, it should be recovered and then recycled safely. Refer to this table provided by the EPA to know the various levels of evacuation for various types of refrigeration.

d) Weigh the refrigerant
If an infusion of refrigerant is required to bring it up to par with recommended levels, ensure that an accurate measure of the refrigerant being added is noted.
e) Document the baseline charge
Record the baseline charge after the recovery or infusion in a logbook for future reference. Statutory regulations applicable, like Section 608 of the EPA, applicable in the United States, ensure that the logbook format is in alignment with the requirements of such compliance.
These steps should help in accurately calculating the baseline charge.
Step-by-Step: Calculate Your HVAC Refrigerant Leak Rate (With Formulas)
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) prescribes two primary methods for calculating refrigerant leaks:

- Annualizing method
It calculates the leak rate based on a yearly projection. This method helps you quantify potential annual refrigerant losses to determine if the leakage is material or otherwise.
- Rolling average method
This method uses a continuous average of leak rates over a specified period, offering a more dynamic and up-to-date assessment of refrigerant leakage.
EPA Annualizing vs Rolling Average Methods: Which Should You Use?
Illustration: Calculating leak rates for a system using both methods
For a better understanding, let's take the example of an air conditioning system with a total refrigerant charge of 1000 pounds. Over the course of a year, 100 pounds of refrigerant were added to the system.
By applying both the annualizing Method and the rolling average method, let’s see how to calculate the leak rates and how the results vary:
Given:
- Amount of refrigerant added: 100 lbs
- Total refrigerant charge: 1000 lbs
- Days since last charge: 6 months
As is evident from the above calculation, annualizing methods show a higher rate than the rolling average.
Although both methods aid in accurately calculating the leak rate, choosing one method is essential. Both methods have a slightly different approach, which results in a high variance. This could influence decision-making and also affect the restoration or retirement of HVAC equipment.
Key considerations for calculating refrigerant leak rates
Calculating refrigerant leak rates accurately isn’t just about compliance; it’s about extending equipment life, reducing environmental harm, and minimizing costly failures.
Here’s what every facility or refrigeration manager needs to consider:
1. Know your system category and leak thresholds
Leak rate limits differ depending on the equipment type:
- Comfort cooling systems: 15% threshold
- Commercial refrigeration: 20% threshold
- Industrial process refrigeration: 30% threshold
These thresholds apply annually and are defined under EPA Section 608. Misclassifying a system can lead to underreporting and non-compliance, so make sure to categorize accurately based on function, not just form.
2. Apply the correct leak rate formula
The standard EPA formula for calculating the leak rate is:
(Amount added / Total charge) × 365 / Days since last refrigerant addition
3. Understand your refrigerant’s compliance profile
Not all refrigerants are created equal:
- CFCs/HCFCs (e.g., R-22): Ozone-depleting and heavily regulated
- HFCs (e.g., R-410A): High GWP and targeted by phasedown regulations
- Low-GWP options (e.g., R-744/CO₂, R-1234yf): May reduce reporting burden but often require specialized handling and monitoring systems
4. Invest in preventive maintenance, not just detection
Preventive maintenance is your first defense. According to the DOE, well-maintained systems can reduce refrigerant loss by 30–50% annually. Schedule quarterly or biannual leak inspections using electronic detectors or ultrasonic tools for early detection.
Pro tip: Log each maintenance session in a centralized refrigeration compliance monitoring software with technician notes, leak test results, and follow-up actions.
5. Only certified professionals can handle refrigerants
EPA regulations mandate that leak testing and handling be done by Section 608-certified technicians. This ensures proper containment, disposal, and repair standards are met.
6. Follow the full EPA compliance workflow
Beyond leak detection, you’re expected to:
- Repair leaks within 30 days (or 120 days if a retrofit/retirement plan is in place)
- Verify repairs with follow-up checks
- Maintain records for at least 3 years, including invoices, test results, and charge logs
- Submit reports for systems exceeding 50 lbs of charge, if thresholds are breached
Skipping even one step can result in fines of $44,539 per day per violation under current EPA enforcement.
7. Don’t include seasonal adjustments in calculations
Adding refrigerant due to seasonal conditions (e.g., summer expansion or winter contraction) does not count toward leak rate calculations—unless you suspect actual system loss. EPA guidelines clarify that seasonal charge variation is exempt if documented appropriately.
Pro tip: Keep seasonal logs separate from leak logs to avoid confusion during audits.
8. Track age, performance, and leak frequency
Leak-prone systems often signal aging infrastructure. Equipment over 10 years old is more likely to leak refrigerants, especially under high-pressure operation. If a system exceeds leak thresholds multiple times a year, it may be more cost-effective to replace rather than repair.
Tip: Use leak rate trends across quarters to flag poor-performing assets early and plan CAPEX upgrades proactively.
9. Use digital tools for centralized, auditable tracking
Spreadsheets create gaps. A CMMS or refrigerant compliance platform that logs refrigerant additions, service activity, technician credentials, and leak history ensures complete traceability.
Leak repair reporting timeline mandated by the EPA
In addition to these, the EPA also mandates specific timelines for repairing and reporting leaks:
- Take immediate action when a significant leak is detected
- If the leak rate is not material, the EPA might grant a timeline of 30 days to fix the leak.
- After repairs, subsequent verification tests should be conducted to confirm effective sealing of the leak.
Leak record-keeping requirements mandated by the EPA
- Leak documentation: Record the date, location, and amount of refrigerant added during each service visit.
- Repair records: Document all repair activities along with dates of detection, repair, or replacement of items, and the methods used for verification testing.
- Compliance reports: Submit annual reports to the EPA or applicable bodies, with comprehensive information on the leak rates, repairs, and refrigerant usage.
How refrigerant leaks harm the environment
It is evident that refrigerant leaks are potent environmental threats and are the drivers of ozone depletion and global warming.
1) Ozone depletion
Many refrigerants like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) contribute to ozone layer depletion.
The 2018 assessment by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reported a continued decrease in ozone-depleting substances in the atmosphere due to CFCs. This has led to several legislations that support controlling refrigerant leaks and the safe handling of refrigerants.
2)Global warming
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are potent greenhouse gases with a high global warming potential (GWP). They trap heat in the atmosphere, kickstarting a spiral of global warming and resultant climate change.
These two major climatic catastrophes in the making call for the need for stringent leak management. In fact, most federal agencies around the world have already started implementing legislation with the objective of controlling refrigerant leaks to prevent further environmental impact.
Regulations to monitor refrigerant leaks and prevent environmental damage
In the United States and worldwide, several regulations are in place to monitor and curb refrigerant leaks and prevent further environmental damage.
Here is an overview:
a) Section 608 and EPA (in the USA)
The most notable legislation in relation to refrigeration has been the regulations laid down by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Section 608 of the EPA mandates the reduction of refrigerant emissions by prescribing methods for refrigerant handling, leak repair, and disposal. It also lists provisions for mandatory leak inspections at regular intervals, prompt leak repairs, and record-keeping for large air conditioning systems.
b) The Kigali Amendment (Montreal Protocol)
The Kigali Amendment (2016) is an amendment to the parent international climate treaty—the Montreal Protocol (1987). The amendment was introduced with the aim of reducing global HFC generation by 80% over the next 30 years.
c) European Union (EU) F-Gas Regulations
Although applicable specifically to the EU region, it is aligned with the objectives of other legislations mentioned previously. The regulation imposes strict requirements for leak checks, proper recovery of F-gases, and training and certification for technicians.
Here is a summary of its requirements:
- Mandatory leak checks at specified intervals help identify and repair leaks promptly, minimizing environmental impact.
- Record-keeping of refrigerant use, leak repairs, and inspections for regulatory reporting.
- Ensuring that technicians are properly trained and certified in handling refrigerants.
Factors influencing HVAC refrigerant leak rate
Both past and present factors influence your HVAC leak rate. Existing conditions in the system, ranging from its initial installation to ongoing maintenance, can impact the leak rate.
1. System age and condition
Older HVAC systems are at higher risk of corrosion of joints and rubber seals, which increases the leak rate.
2. Installation quality
Poor installation, like using cheap evaporator coils, copper tubes, or inconsistent welding, can lead to refrigerant leaks.
3. Refrigerant type
Using low-GWP alternatives or improper combinations of chemical refrigerants can increase the leak rate.
4. Operating conditions
If the air conditioning system is exposed to extreme climatic conditions like sunlight or rain, it can increase the risk of corrosion, increased wear and tear, and subsequent leaks.
5. Technician expertise and training
Technicians who are not qualified or experienced in installation, maintenance, or repair can cause damage to the system and increase the chance of leaks.
6. Regulatory compliance and monitoring
The choice of leak rate calculation as mandated by regulatory compliance can influence the leak rate.
7. Maintenance practices
Irregular maintenance and inspection practices, including leak checks, repairs, and replacements, can improve or degrade the HVAC system’s longevity.
The true cost of refrigerant leaks in the US retail industry
Retail businesses—especially supermarkets, grocery chains, and cold storage facilities—face serious financial and operational risks from refrigerant leaks.
You should understand that these aren't just minor inefficiencies; they affect everything from your bottom line to brand reputation and environmental compliance.
How much do leaks cost you directly?
1. Cost of refrigerant losses
Stores using high-GWP refrigerants like R-404A can lose up to 700 pounds annually, translating to $5,000 per store per year at $7 per pound. Multiply that across locations, and you’re looking at a six-figure drain on your margins. 🔗 Source – Copeland
2. Refrigerant leak repair cost
The cost to repair a refrigerant leak depends on the system’s complexity, the location of the leak, and service availability. On average, refrigerant leak repair costs range from $100 to $1,500 per incident for commercial HVAC or refrigeration systems. In urgent cases or for hard-to-access leaks, the price can go even higher. 🔗 Source – Excel Mechanical
3. Refrigerator gas leak repair cost (for smaller systems)
In smaller refrigeration units, such as those used in retail backrooms or convenience stores, the gas leak repair cost typically ranges between $150 and $400, depending on the refrigerant used and the severity of the leak. Though lower in absolute cost, the frequency of leaks can add up quickly across multiple locations.
4. Spoiled inventory and downtime
Failed refrigeration = spoiled products. A single case failure during peak summer can cost thousands in perishable inventory, not to mention damage to brand trust and compliance headaches.
Hidden costs that drain profits over time
1. Higher energy bills: A leaking system works harder to maintain set temperatures. Even a 10% drop in refrigerant levels can cause a 10–20% increase in power consumption, adding significant OPEX costs. 🔗 Source – Watkins Heating & Cooling
2. Environmental compliance risks: Refrigerants like R-404A have a Global Warming Potential (GWP) of nearly 4,000. Leaks not only harm the environment but may trigger penalties under EPA Section 608 and state-level rules like CARB in California.
3. Equipment wear and tear: Running systems with low refrigerant lead to compressor strain, ice buildup, and system inefficiencies, which can shorten equipment lifespan and inflate capital expenses.
What does this look like at scale for your business?
1. Chain-level financial impact: A 100-store chain losing refrigerant at average rates could face over $500,000 in leak-related costs annually, excluding service and spoilage losses.
2. Industry-wide savings potential: If all U.S. supermarkets achieved the leak rates of EPA GreenChill Partners, the industry could save $108 million in refrigerant costs annually, not to mention avoiding 27 million metric tons of CO₂e emissions.
How to fix refrigerant leakage issues in the retail industry
✔️ Proactive leak detection: Use continuous monitoring and IoT-enabled alerts to catch leaks early, before they become major costs.
✔️ Scheduled preventive maintenance: Adopt a routine maintenance program to inspect seals, valves, and pressure levels regularly.
✔️ Immediate leak repair protocols: Don’t delay. Rapid response reduces refrigerant waste and prevents costly product loss.
✔️ Join EPA’s GreenChill Partnership: Get recognized for sustainability leadership and access best practices, benchmarking, and tools to reduce leak rates, lower emissions, and save money. 🔗 Learn More – GreenChill Partnership
And while these best practices are essential, having the right platform can make a world of difference.
But leak detection is only part of the puzzle. To truly stay ahead of costs, compliance risks, and system inefficiencies, you need to start with the foundation: accurately managing refrigerant charge.
🧊 What is refrigerant charge?
Refrigerant charge refers to the total amount (by weight) of refrigerant in a cooling system. This includes the refrigerant within the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and all connecting piping.
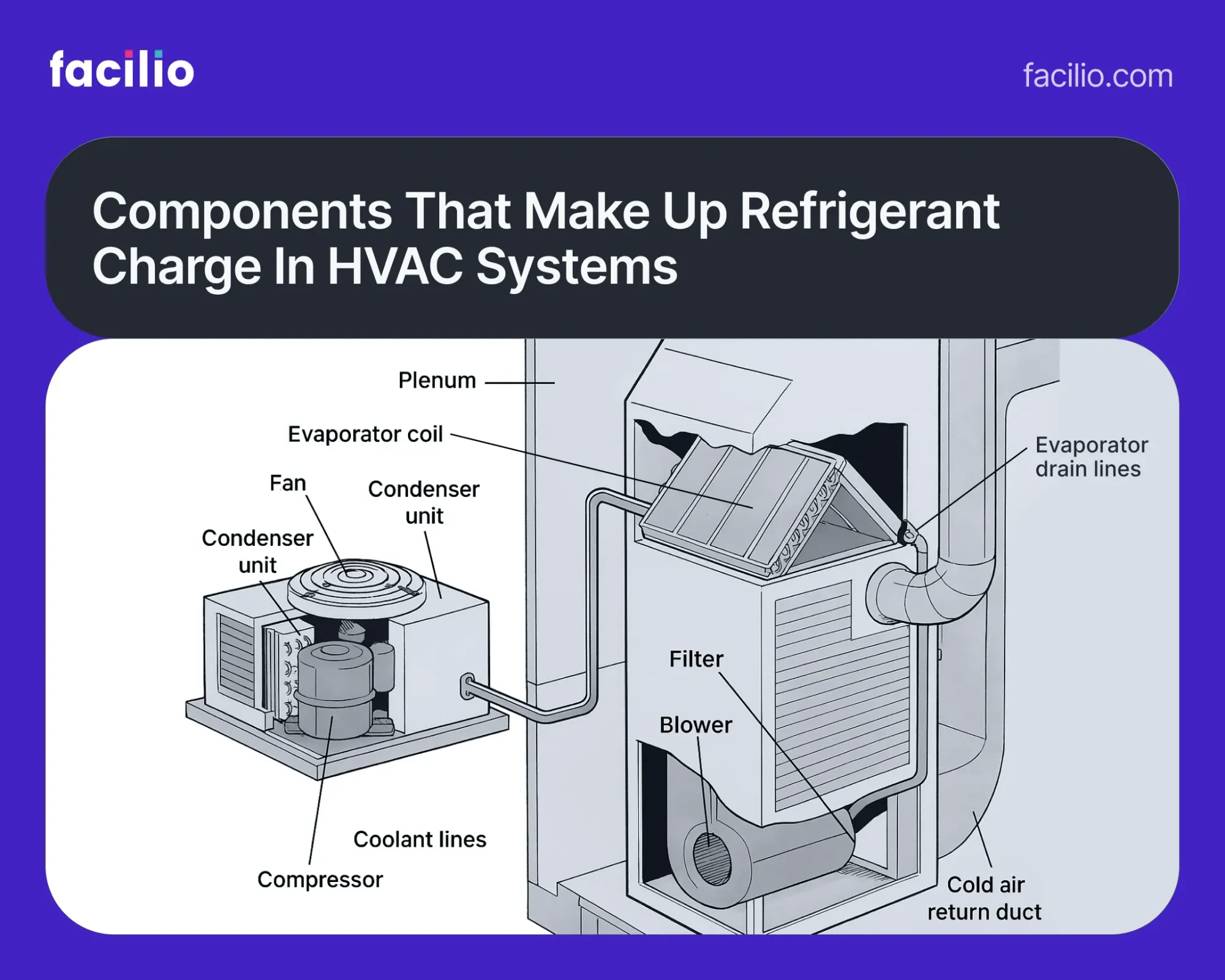
It’s typically measured in pounds or kilograms and varies based on system size, design, and configuration.
For commercial HVAC and refrigeration systems, refrigerant charge isn’t a fixed number—it must be measured, tracked, and documented accurately.
Over time, small losses from leaks or service activities can go unnoticed, impacting both performance and compliance. That’s why charge data is foundational to refrigerant management programs.
⚠️ Why it matters more than you think
An accurate refrigerant charge is critical for four key reasons:
- Energy efficiency: Both undercharging and overcharging cause systems to work harder, consuming more power while delivering less cooling.
- Equipment health: Improper charge puts stress on compressors, leads to coil freezing or overheating, and reduces asset life.
- Regulatory compliance: EPA refrigerant leakage rate thresholds are calculated as a percentage of the total charge. If your charge number is wrong, your reported leak rate will be too.
- Environmental impact: Every pound of leaked refrigerant can equal thousands of pounds of CO₂e. A poorly managed charge contributes directly to emissions and fines.
Put simply, refrigerant charge isn’t just a service metric—it’s the baseline for operational, financial, and environmental performance.
How refrigerant leakage rate calculations impact refrigerant charge
Leak rate calculations rely entirely on one critical number: your documented full system charge. According to the EPA, leak rate = (refrigerant added ÷ full charge) × 100.
So even if your leak is small, an underestimated charge will inflate the calculated leak rate, potentially triggering false compliance violations.
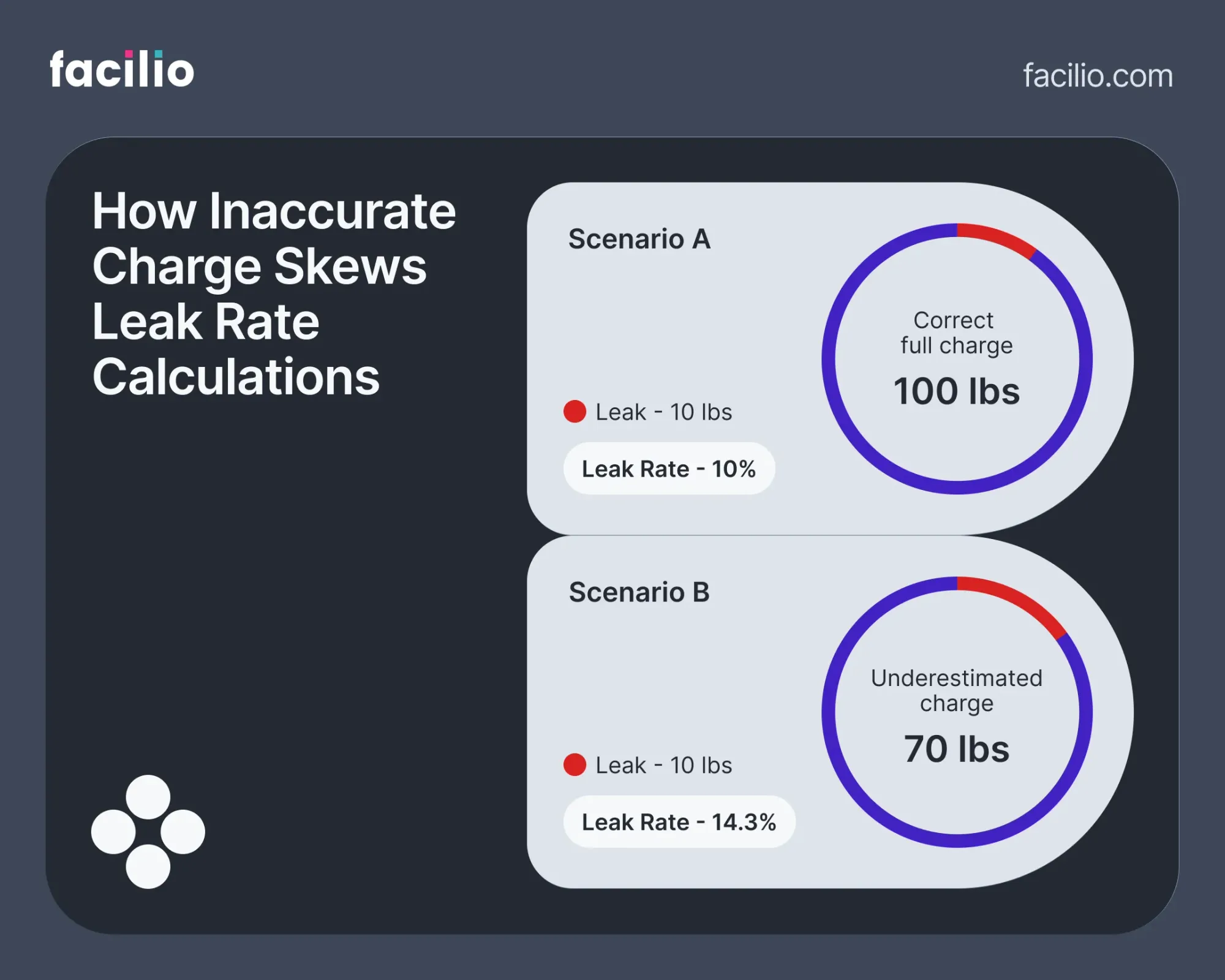
Many operators rely on equipment nameplates to define charge, but research shows these values can underreport by 20–70%. That means:
- Your “calculated” leak rate may appear worse than it actually is,
- You could be flagged for regulatory action,
- And you're making O&M decisions based on faulty data.
For accurate leak tracking, energy monitoring, and EPA reporting, your refrigerant charge must reflect the true, as-built system volume—not a theoretical estimate.
✅ Best practices for managing refrigerant charge across sites
Managing refrigerant charge at scale requires more than manual logs or periodic inspections. Here’s how multi-site teams can stay ahead:
✔️ Establish a verified baseline per system: Weigh cylinders during installation or recharge and account for all refrigerant-bearing components—not just what’s listed on the nameplate.
✔️ Track every charge event in your CMMS or RMS: Log refrigerant additions, removals, and transfers in real time. This historical data is essential for compliance audits and leak investigations.
✔️ Use IoT sensors or RMS platforms for continuous monitoring: Connected tools can detect refrigerant level drops early and alert teams before performance degrades or leaks escalate.
✔️ Standardize charge management protocols across all locations: Ensure every site follows the same charge verification, logging, and reporting process to reduce discrepancies and avoid missed compliance windows.
✔️ Audit refrigerant data quarterly: Compare live readings with expected charge levels. Look for deviations that suggest unreported leaks or technician-related overfills.
Managing refrigerant charge across multiple sites takes more than refrigerant leak rate calculation spreadsheets or periodic checks—it demands connected visibility, automated workflows, and smart alerts.
That’s precisely where Facilio’s platform makes the difference.
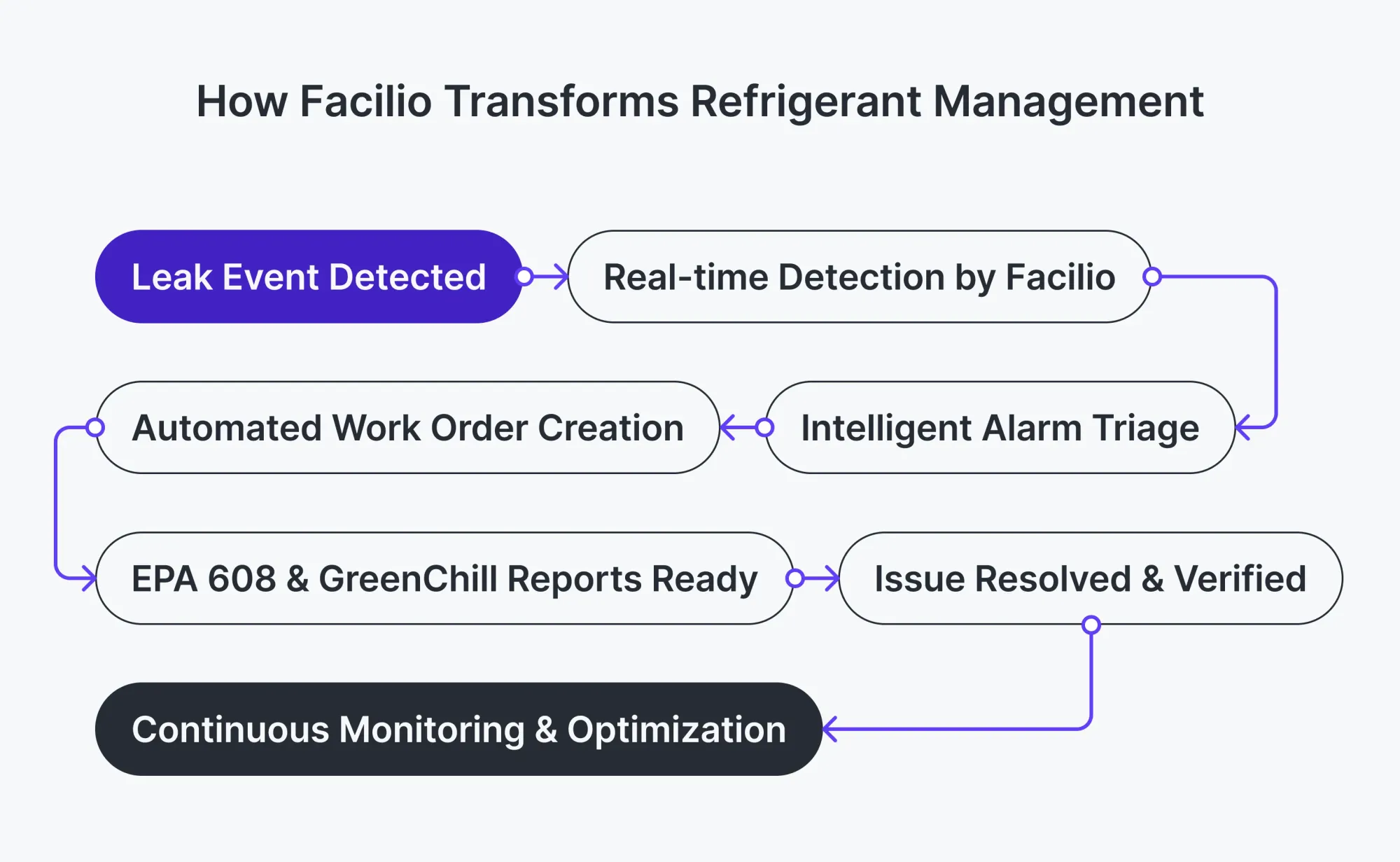
Facilio’s Connected Refrigeration Platform: End-to-End Refrigerant Management at Scale
Refrigerant compliance isn’t just about spotting leaks—it’s about controlling the entire lifecycle of your refrigerant charge, from install to inspection to incident response. Facilio helps you stay ahead on all fronts—preventing costly leaks, avoiding compliance penalties, and optimizing HVAC performance.
Here’s how Facilio supports your refrigerant charge strategy:
✅ Monitor Refrigerant Charge in Real Time: Get a continuous view of refrigerant levels across every asset and site—so you can detect deviations before they become compliance issues or cooling failures.
✅ Centralize Charge Logs and Leak History: Track every top-up, removal, and leak event in a single dashboard. No more paper logs or fragmented data across stores.
✅ Automate Leak Detection and Alerts: Facilio’s IoT sensors and smart rules engine detect abnormal charge drops instantly, allowing your team to respond before product loss or equipment damage occurs.
✅ Stay Audit-Ready, Always: Generate EPA, F-Gas, and GreenChill-compliant reports automatically, with timestamps and full refrigerant history—ready for inspections at a moment’s notice.
✅ Cut Costs, Reduce Waste, Extend Asset Life: By maintaining optimal charge levels and resolving leaks early, you reduce energy use, protect equipment, and extend asset lifecycle—all while meeting your sustainability goals.
How Tuten Labs Transformed Refrigerant Management with Facilio
Tuten Labs, managing over 10,000 retail stores across North and Latin America, was dealing with slow service and constant alarm fatigue due to old-school processes.
After switching to Facilio’s AI-driven Connected Refrigeration platform, they automated work orders, improved refrigerant monitoring, and cleaned up alarm triaging.
The result?
A 10-15% drop in customer service calls and smoother operations. With real-time insights and faster issue resolution, Tuten Labs now stays compliant and saves money across the board.
The Bottom Line
Calculating leak rates accurately is essential, but monitoring them proactively is even more critical.
With Facilio, you don’t just meet compliance—you optimize efficiency, cut costs, and future-proof your HVAC operations.
Why wait?
Take control of your refrigerant management today.
Stay ahead of the industry and ever-evolving EPA regulations with Facilio
Schedule My Demo NowFAQs – HVAC refrigerant leak rate calculation
Q: What is a refrigerant leak rate calculator?
A refrigerant leak rate calculator is a tool used to determine the rate at which refrigerant is leaking from an HVAC system. By calculating the leak rate, facility managers can identify potential issues early, take corrective actions, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Q: What are the benefits of using a refrigerant leak rate calculator?
Using a refrigerant leak rate calculator offers several benefits, such as:
- Early detection of leaks that could otherwise lead to extensive damage and costly repairs.
- Compliance with environmental regulations by accurately monitoring and reporting leak rates.
- Maintain optimal HVAC system performance by ensuring the correct refrigerant charge.
- Cost savings are achieved by reducing the need for frequent refrigerant recharges and lower energy costs through improved system efficiency.
Q: What are the methods for calculating refrigerant leakage rates?
The two primary methods for calculating refrigerant leakage rates are:
- Annualizing Method: This method projects the refrigerant leakage rate per year based on the amount of refrigerant added and the time since the last charge.
- Rolling Average Method: This method calculates the average leak rate over a specified period, typically one year, to provide a continuous assessment of system performance.
Q: How often should refrigerant leakage rates be calculated?
Refrigerant leakage should be calculated and monitored at three crucial junctures:
- During routine maintenance
- After adding refrigerant
- Whenever a leak is suspected
Q: How do you calculate the leakage rate?
Leakage rate is calculated using EPA-prescribed formulas: either the annualizing method or the rolling average method. Both require you to know the amount of refrigerant added and the system’s total charge. The result is expressed as a percentage of the total charge lost over a specified period.
Q: What is the EPA leak rate for refrigerant?
The EPA sets maximum allowable leak rates based on system type: 20% per year for comfort cooling, 30% for commercial refrigeration, and 30% for industrial process refrigeration. Exceeding these thresholds requires prompt repairs and regulatory reporting.
Q: What is the average refrigerant leakage rate?
Average leak rates vary by industry and maintenance practices. In U.S. supermarkets, typical leak rates range from 15% to 25% annually, but best-in-class operations (like GreenChill Partners) achieve rates below 10% per year.
Q: What is the acceptable leakage rate?
Acceptable leak rates are those that remain below the EPA thresholds for your system type. Lower rates are always better for both compliance and cost—aim for under 10% annually for best sustainability and operational performance.
Q: What triggers the requirement to calculate the leak rate?
You must calculate the leak rate whenever refrigerant is added to a system (except for seasonal adjustments), during routine maintenance, or if a leak is suspected. EPA regulations require documentation whenever system servicing involves refrigerant recharge.
Q: What are the EPA refrigerant rules for 2025?
The EPA’s 2025 rules require stricter leak rate thresholds, more rigorous recordkeeping, and expanded refrigerant phase-downs for high-GWP gases. Regular leak inspections, prompt repairs, and detailed documentation are now mandatory for most commercial and industrial systems.
Q: How can Facilio help with refrigerant leak rate calculations?
Facilio offers comprehensive solutions to assist with refrigerant leak rate calculations:
Here’s how Facilio can help:
- Proactive monitoring and control of leaks
- Seamless integration with all related facility management tools
- Assured compliance with regional and global environmental regulations
- Drive sustainability at scale through automation
More from Facilio















